The theory of planned behavior (TPB) is very similar to that of the one which slightly preceded it and that is the theory of reasoned action. Although these two theories came during a different timeline, they predominantly hold the same assumptions about behavior. TRA and TPB believed that behaviors are influenced by intentions and intentions are created from attitudes.
History Of How The Theories Came By
Fishbein and Azjen initially proposed the theory of reasoned action in 1967 during a time when there was a big discrepancy between attitude and behavior. Although some theories attempted to explain the relationship between the two, they didn’t turn out successful. The theory of reasoned action successfully explained the relationship and asserted that behavioral intentions play a key role in behaviors. TRA also put forth the factors which determine the adoption of intentions which are attitudes and subjective norms.
A few years down the line, Fishbein and Azjen decided to review the theory of reasoned action and wanted to improve the predictive power of the theory. Therefore they added another important determinant to the theory called perceived behavioral control which refers to the extent to which a person believes they are capable of performing a behavior and named it the theory of planned behavior (TPB).
However, both TRA and TPB gave a substantial number of positive results to prove their efficacy and hence this theory was widely accepted by many researchers and theorists in instilling behavioral change. This theory was successfully able to predict and bring significant changes in areas such as health behaviors including smoking, drinking, exercise, sun protection, breastfeeding, substance use, use of contraceptives, safety helmets, seatbelts etc.
The Theory Of Reasoned Action (TRA)
This theory assumed that intentions are the ultimate driving forces of a behavior. Before any behavior takes place, it is preceded by a period of deliberate planning of the behavior based on the attitude and consequences. A person would only act upon something if they have a positive attitude and implications about the behavior.
For example, Joshua chose to live a healthy lifestyle because he believes it is the most rewarding way to live life and also because adopting such a lifestyle would keep him fit and healthy at a physical and mental level.
TRA also proposes that intentions are a result of two essential factors and they are underlying attitudes about the behavior and subjective norms. Attitudes are personal opinions and thoughts about a specific behavior. Attitudes could either be positive or negative.
For example, many people across the world hold a negative attitude about any form of abuse and hence try to keep away from it.
Subjective norms refer to the social appropriateness of any behavior. Although a person likes a behavior, they may not choose to act upon it because it is considered undesirable by society.
For example, wearing colorful attire for a funeral might be frown upon by the members of society as it is a place of bereavement and any color other than black or white might give out wrong messages otherwise.
As this theory doesn’t discuss the volitional control that a person possesses which would adopt that behavior, this theory gives out a somewhat incomplete feeling.
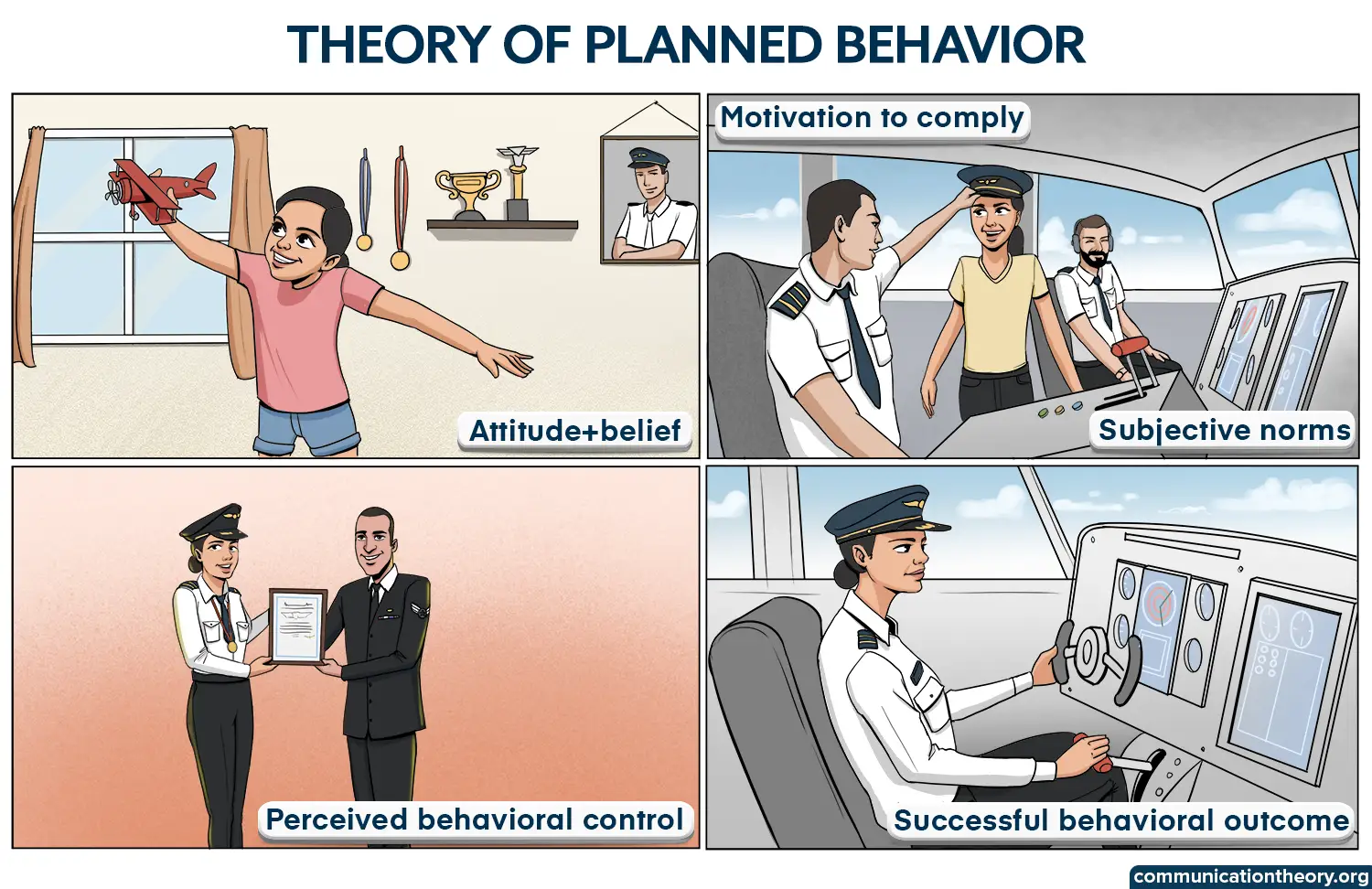
The Theory Of Planned Behavior (TPB)
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) is nothing but an extension of the theory of reasoned action. In this theory, an additional component of perceived behavioral control gives it a higher predictive power and completeness.
The inclusion of perceived behavioral control stems from the idea that behaviors are influenced by behavioral intention and the perceived ability to perform.
What Is Perceived Behavioral Control?
In simple terms, perceived behavioral control is nothing but the amount of control a person believes they possess over a behavior. It is a personal perception about how much they hold a certain amount of charge over a specific behavior.
For example, when Reynold went for the final examination he was confident because he believed that he had prepared well and he could answer any question even if they were framed tricky.
TPB postulates that perceived behavioral control is an independent factor even if the other two factors are kept constant. Even if attitudes and subjective norms are kept constant, the perception of one’s ability to exercise control over a behavior will influence the behavior nevertheless.
For example, Lauren wanted to take a solo trip across the world and he got support and acceptance from the people around him. But he was still apprehensive because he wasn’t sure if he would be able to handle the changes in climate, food and time zone.
The Integrated Behavioral Model
As the name suggests, the Integrated Behavioral Model is an integrated approach to understanding the motivation behind human behavior. After TRA and TPB came by, theorists were looking to construct a model that would be inclusive of the findings made by Fishbein and Azjen and other theories which would provide a detailed explanation of determinants of behavioral intentions.
IBM attaches four determinants of behavioral intentions.
1. Skill Set:
Although a person may have the right intention to take up any task, they should also possess the required knowledge and skill set to pursue any action.
For example, Irin aspired to become a pilot and she wanted to commit herself to it and give it her all. But she realized she didn’t possess the required skill to pursue her flying profession. Hence, she decided to take up a course which would make her equipped for the venture.
2. Environmental Constraints:
Any form of environmental constraints or barriers may not facilitate a behavior. Therefore the behavior shouldn’t face any obstacles from the environment.
Although Irin had the right intention, she faced many criticisms from her parents and people around her citing the reason that it is a risky profession to desire.
3. Salience:
The behavior should be important for the person. Any insignificant behavior would be hard to sustain and would therefore fizzle out in a short span.
Despite the criticisms and difficulties, Irin was headstrong about her decision because it was her dream to fly an aircraft someday. She took the necessary steps which would take her to the place she aspired.
4. Habitual behavior:
If a certain behavior has been practiced for a considerable amount of time, it would evolve into a habit and take place involuntarily. So intentions aren’t consciously reiterated every single time the task is done.
Once Irin became a pilot, flying became her full-time job. So her intention to fly a plane didn’t keep revisiting every time she flew because it became more of a routine.
Strengths And Limitations Of TPB
TPB is considered as a better and more evolved than TRA as it houses an important determinant of behavioral intention which is perceived behavioral control. This makes it a more efficient predictor of behavior.
For example, research shows TPB was used to successfully predict the leisure activity intentions and behaviors of college-going students. Results from another study exhibit that TPB was also able to predict drivers’ compliance with speeding limits. This theory was also efficiently applied in predicting hunting intentions and behaviors.
Regarding limitations, many scholars criticize that this theory ignores the situational needs of a person. Although a person might have a positive attitude about a behavior, due to their current needs they might decide to not pursue a task.
For example, Meg likes to visit the church every Sunday. But on one Sunday, she couldn’t do so because she had an appointment with her physician.
Another limitation is that TPB doesn’t integrate the role of emotions in the development of intentions which would otherwise make the theory more comprehensive and whole.
Difference Between The Theory Of Reasoned Action TRA And The Theory Of Planned Behavior TPB
The most important difference between TRA and TPB is the number of determinants of intentions. TRA assumes that the determinants of intentions are attitudes about the behavior and subjective norms. But TPB went ahead to further add one more determinant which is perceived behavioral control.
Another difference between the two theories is the predictive capability of the theory. TRA is only capable of predicting behaviors to some extent. Whereas TPB has a better predictability factor, especially in the field of health.
How Is Perceived Behavioral Control Related To Self-Efficacy?
Although perceived behavioral control and self-efficacy seem to be very similar because they both to some extent refer to the ability of a person to perform a task, they are two distinct concepts. The difference here is that perceived control is more of the amount of control a person has over a behavior despite the opposing external factors. And self-efficacy is more of evaluating a person’s potential to perform a behavior.
For example, to say “It seems difficult to maintain my relationship with him” is perceived behavioral control and to say “I know I’m finding it hard to maintain my relationship with him, but I’m confident that I can do something about it” is self-efficacy.
Earlier theories related to health, perceived control over behavior as efficacy because the occurrence seems very frequently overlapping.
Applications Of TPB In The Health Sector
As mentioned before, TPB shows higher prospects in terms of predicting human behaviors in the area of physical health. TPB has been successfully able to predict many health-related behaviors such as dieting, use of contraceptives, choice of leisure activities etc.
The elements of this theory have also been applied in nutrition-based intervention programs where participants were encouraged to consume more fruits and vegetables using the constructs of TPB. Results of the study reveal that there was an increase in the intake of fruits and vegetables after being exposed to the intervention program.
A study conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of TPB in predicting health behavior has confirmed its effectiveness. The results of the study also showed that attitude towards the behavior and perceived behavioral control were the two significant factors behind behavioral intentions.
When TPB and IBM were cohesively applied to understand alcohol-related behaviors, it was found that the constructs of TPB such as attitude were backed up by intention which was the strongest predictor of alcohol-related behavior.
Another study conducted to predict the cervical cancer screening among Latinas using TPB found that subjective norms and perceived behavioral control were positively correlated to do the screening among other constructs. Hence, TPB holds well in effectively predicting the screening behavior of Latinas.
The concept of TPB can be well explained using the current crisis of taking up Covid vaccination:
| S. No. | Constructs of TPB | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Intention | I have to get vaccinated for Covid as early as possible. |
| 2. | Attitude | I believe getting vaccinated for Covid is an absolute necessity. |
| 3. | Subjective norms | All my family members and friends think of it positively and got themselves vaccinated too. |
| 4. | Perceived behavioral control | I believe that I can get myself vaccinated by contacting the relevant people and getting the required information regarding the vaccination. |